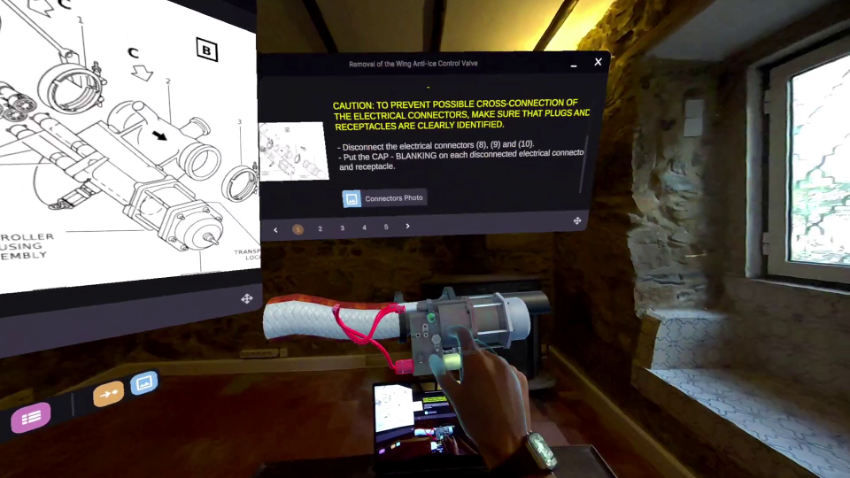
The air transportation industry faces significant challenges nowadays in maintaining high safety standards and providing timely aircraft maintenance technician (AMT) training. Most importantly, this industry must meet strict regulatory requirements, prevent unscheduled equipment failures and deal with shortage of workers, many in advanced age according to a previous report of the Aeronautical Repair Station Association [1]. In addition, as aircraft systems become more complex, the demand for advanced training tools like XR-based solutions has increased.
A critical element of the Minimum Equipment List is the Wing Anti-Ice Valve (WAIV) that must be working for the airplane to operate safely. Failure in the WAIV leads to extended grounding times, while repairing also requires specialized maintenance procedures.
XR5.0 aims to address this issue by providing a solution for training AMTs to properly disassemble the WAIV through an interactive XR environment. This solution allows AMTs to practice each step of the disassembly process in a realistic 3D simulation, providing detailed guidance on safety procedures, tools and the correct steps to dissemble this component. This solution is tailored to each user based on the profile (experience) and performance metrics (execution time, errors). XR5.0’s AMT Virtual Training aims to improve technicians’ skills and to reduce the likelihood of errors by providing a customized and hands-on virtual training.
The choice of XR technology is driven by the advantages it offers in visualizing and interacting with complex objects. XR-based visualizations provide a more intuitive understanding of visual information [2], allowing AMTs to see the WAIV from multiple angles and levels of detail. This immersive approach is especially valuable for this procedure where AMTs must understand complex mechanical parts and steps to perform WAIV maintenance accurately.
The inclusion of 3D manipulation and interaction in XR environments improves the training experience by simulating the motor coordination and interactions users experience in real-world settings [3]. These features allow AMTs to inspect the different components that represent the actual physical tasks. The intuitive interaction in such XR environments will help trainees get familiarity with the equipment, potentially contributing to skill refinement and confidence when performing the task in the real environment.
Key Features of the XR5.0 AMT Virtual Training Solution
a) Personalization/Adaptation
This feature focuses on adapting the training experience to each user. The application will provide a priori personalization and real-time adaptation of content according to the user profile which ensures that the training is tailored for the level, background, and specific needs of the technician.
b) XR-based Training
This feature offers a step-by-step virtual guide to support technicians to complete maintenance procedures. This guide is structured to provide users with information for each step of the task, using different materials such as text and images from PDF manuals or even videos to detail specific steps in the procedure.
c) 3D Visualization Tool
The 3D visualization tool allows users to visualize and interact with a virtual model of the WAIV, promoting a better understanding of the equipment’s structure and function. Additionally, this component also contains the virtual models of tools and equipment including tool selection and manipulation, which helps ensure user familiarity with each step in the procedure.
d) AI Voice Assistant
The application includes a speech-based voice assistant equipped with procedural knowledge. It uses a specific knowledge database to answer in real-time to the operators’ questions, providing verbal guidance and feedback.
In sum, the XR5.0 AMT Virtual Training combines various features as step-by-step guidance, 3D visualizations and AI-driven tools to train AMTs through a multi-faceted approach. The solution provides detailed instructions with real-world context to help AMTs for competence development, improve procedural accuracy, and confidence in performing maintenance tasks, making it a valuable tool for both off-the-job and on-the-job training of AMTs.
References:
[1] ARSA (2022). Not Enough Aviation Mechanics: How the industry can address this decade’s shortage in aircraft maintenance workers. Retrieved from: https://arsa.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/OW-2023WorkforceAnalysis-Technicians.pdf
[2] Abrash, M. (2021). Creating the Future: Augmented Reality, the next Human-Machine Interface. 2021 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IEDM19574.2021.9720526
[3] Sundstedt, V. & Garro, V. (2022) A Systematic Review of Visualization Techniques and Analysis Tools for Eye-Tracking in 3D Environments. Front. Neuroergon. 3:910019. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnrgo.2022.910019